Conditions
Varicose Veins
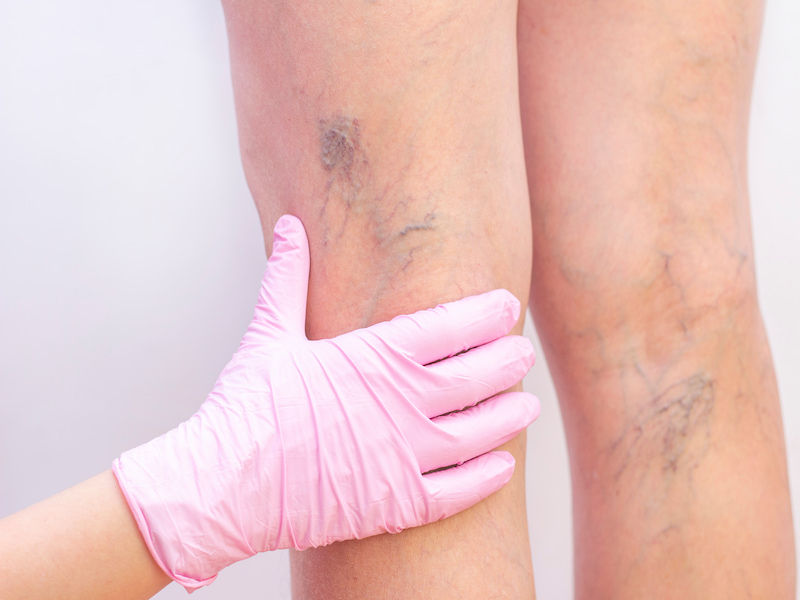
Varicose veins are enlarged blood vessels that bulge just beneath the skin’s surface. They can vary in size and are typically blue or purple in colour. These veins become enlarged due to the weakening of the vein walls and the poor functioning of the valves inside the veins (incompetent valves).
Varicose veins are often more noticeable when standing up and may disappear when lying down.
Spider veins
Spider veins are dilated, small blood vessels that seem near the surface of the skin, frequently creating web-like patterns on the face, legs, or other locations. While typically harmless, they can sometimes indicate underlying venous insufficiency.
Dr. Soroush Sohrabi in Dubai effectively eliminates spider veins with advanced, minimally invasive treatments, improving both appearance and vascular health. We provide safe and long-lasting results with individualized care specifically designed for each patient.
Leg Ulcers
Venous leg ulcers are chronic, non-healing wounds that develop due to poor venous circulation. They are the most common type of leg ulcer, primarily caused by chronic venous insufficiency (CVI).
If left untreated, venous ulcers can lead to severe complications, recurrent infections, and impaired mobility. Early diagnosis and proper treatment can greatly enhance healing results.
Thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis refers to both inflammation of a vein and the formation of a blood clot within it. This condition most commonly affects superficial veins, leading to superficial venous thrombophlebitis. Symptoms often include pain, tenderness, and swelling along the affected vein, which may appear red, firm, and warm area on the skin. The presence of a clot can also impair blood flow, potentially causing further complications if left untreated.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Definition of deep vein thrombosis Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot develops within the deep veins, most commonly in the legs. This clot, known as a thrombus, can obstruct normal blood circulation, leading to symptoms such as leg swelling and pain.
Unlike superficial venous thrombosis, DVT carries a higher risk of serious complications, including pulmonary embolism, making early detection and treatment essential. For those seeking DVT diagnosis & treatment in Dubai, specialized care is available.
Skin Changes with Varicose Veins
Varicose veins can lead to progressive skin changes, particularly in the lower legs, due to chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). As blood pools in the veins and pressure increases, the skin may undergo discoloration, thickening, and inflammation, often indicating worsening vein disease.
Early symptoms include dryness, itching, and mild pigmentation (skin discoloration), but more severe changes such as venous eczema, lipodermatosclerosis (skin hardening), and ulceration may develop over time.
Lymphedema
The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance, immune function, and circulation. When lymphatic vessels are damaged or blocked, fluid accumulates in the tissues, leading to swelling, discomfort, and skin changes. Understanding this condition is the first step towards effective lymphedema treatment in Dubai.
Leg Edema (Swelling)
Dr. Soroush Sohrabi in Dubai assesses and treats venous causes of leg edema using advanced diagnostic methods and personalized treatment plans. Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is the leading cause of leg edema, accounting for approximately 70% of cases.
Venous insufficiency occurs when leg vein valves become weak or damaged, leading to blood pooling and increased pressure in the veins.This leads to fluid leakage into surrounding tissues, resulting in swelling, heaviness, and discomfort.
Lipedema
Lipedema is a chronic disorder that causes the abnormal buildup of painful, fatty tissue, usually in the legs and sometimes the arms. It mainly affects women and is often mistaken for simple weight gain or lymphedema. Unlike ordinary fat, lipedema tissue is symmetrical, tender to touch, and resistant to diet or exercise. Over time, it can cause heaviness, bruising, and reduced mobility. As a UK-trained Consultant Vascular & Endovascular Surgeon practising in Dubai, Dr. Soroush Sohrabi offers expert assessment and management of lipedema, helping patients receive an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan that improves comfort, mobility, and quality of life.
Critical Leg Ischemia
Critical Leg Ischemia (CLI) is a severe form of Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) in which blood flow to the legs is critically reduced. This lack of circulation leads to persistent rest pain, non-healing ulcers, or gangrene, often requiring urgent medical attention. The condition occurs when arteries become severely narrowed or blocked by atherosclerosis, preventing enough oxygen and nutrients from reaching the tissues. Without timely intervention, CLI can lead to tissue loss and amputation. Diagnosis typically involves vascular imaging such as duplex ultrasound or angiography, and treatment may include angioplasty, stenting, bypass surgery, or advanced endovascular procedures to restore blood flow and preserve limb function
Diabetic foot
Diabetic Foot refers to a range of complications that affect the feet of people with diabetes, caused by a combination of poor circulation, nerve damage (neuropathy), and reduced ability to heal. These changes increase the risk of ulcers, infections, and in severe cases, gangrene or amputation. Early warning signs include numbness, tingling, foot deformities, or wounds that do not heal. Proper foot care, regular vascular and neurological assessment, and prompt treatment of any wounds are essential to prevent serious complications. Advanced management may include blood flow restoration through angioplasty or bypass surgery, infection control, and multidisciplinary care to preserve limb function and prevent recurrence.
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA)
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) is a condition in which the main artery in the abdomen (aorta) becomes enlarged and weakened, increasing the risk of rupture and life-threatening internal bleeding. The condition often develops silently over many years and is commonly linked to atherosclerosis, smoking, high blood pressure, and family history. Most AAAs are discovered incidentally during imaging for other reasons. When detected early, regular monitoring and risk factor control are essential. Larger or rapidly expanding aneurysms may require intervention through endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) or open surgical repair, procedures designed to reinforce the vessel wall and prevent rupture.
Intermittent Claudication
Intermittent Claudication is a common symptom of Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), characterised by pain, cramping, or fatigue in the legs during walking that improves with rest. It occurs when narrowed or blocked arteries reduce blood flow to the leg muscles, limiting oxygen supply during activity. The pain typically affects the calves but may also involve the thighs or buttocks. Intermittent claudication is an early warning sign of systemic atherosclerosis and should not be ignored. Diagnosis usually involves ankle-brachial index testing and vascular imaging, while treatment focuses on lifestyle modification, exercise therapy, medication, and in some cases angioplasty or stenting to restore circulation and improve walking distance.
Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid Artery Disease occurs when the carotid arteries in the neck — the main vessels supplying blood to the brain — become narrowed or blocked by a buildup of fatty deposits (plaque). This condition significantly increases the risk of stroke or transient ischaemic attack (TIA). Many patients do not experience symptoms until a serious event occurs, but warning signs can include brief weakness, numbness, or vision loss on one side. Diagnosis is made through Doppler ultrasound, CT angiography, or MR angiography to assess the degree of narrowing. Treatment depends on the severity and may include medication, lifestyle modification, carotid endarterectomy, or carotid artery stenting to restore healthy blood flow and prevent stroke.




.webp)


%20(1).webp)




.webp)
